Biodegradation of azo dyes acid red 183, direct blue 15 and direct red 75 by the isolate Penicillium oxalicum SAR-3.
Samta Saroj, Karunesh Kumar, Nidhi Pareek, R Prasad, R P Singh
Index: Chemosphere 107 , 240-8, (2014)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Soils contaminated with dyes were collected and screened for obtaining potential fungal strains for the degradation of azo dyes. A strain that demonstrated broad spectrum ability for catabolizing different azo dyes viz. Acid Red 183 (AR 183), Direct Blue 15 (DB 15) and Direct Red 75 (DR 75) at 100 mg L(-1) concentration was subsequently identified as Penicillium oxalicum SAR-3 based on 18S and internal transcribed spacer (ITS) rDNA gene sequence analysis. The strain has shown remarkably higher levels of degradation (95-100%) for almost all the dyes within 120 h at 30°C at pH 7.0. Notable levels of manganese peroxidase (659.4 ± 20 UL(-1)) during dye decolorization indicated the involvement of this enzyme in the decolorization process. The dyes following decolorization were catabolized as evident by spectroscopic analyses.Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
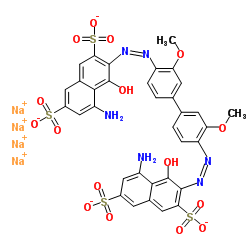 |
C.I. Direct Blue 15
CAS:2429-74-5 |
C34H24N6Na4O16S4 |
|
Chemical-induced atrial thrombosis in NTP rodent studies.
2005-01-01 [Toxicol. Pathol. 33(5) , 517-32, (2005)] |
|
CI Direct Blue 15.
1993-01-01 [IARC Monogr. Eval. Carcinog. Risks Hum. 57 , 235-45, (1993)] |
|
Catalytic wet peroxide oxidation of azo dye (Direct Blue 15)...
2011-03-15 [J. Hazard. Mater. 187(1-3) , 348-54, (2011)] |
|
Decolourization of direct blue 15 by Fenton/ultrasonic proce...
2013-05-01 [Ultrason. Sonochem. 20(3) , 970-7, (2013)] |
|
Decolorisation and detoxification of Direct Blue-15 by a bac...
2007-11-01 [Bioresour. Technol. 98(16) , 3168-71, (2007)] |