| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Calcium chloride
CAS:10043-52-4 |
|
 |
DL-Serine
CAS:302-84-1 |
|
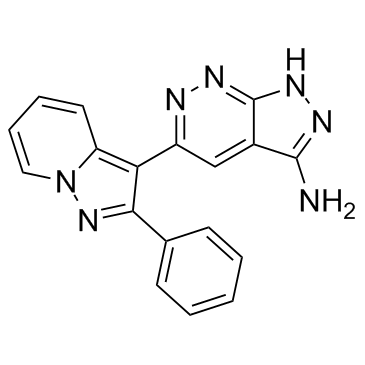 |
FR 180204
CAS:865362-74-9 |
|
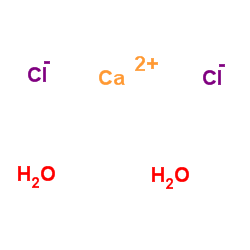 |
calcium chloride dihydrate
CAS:10035-04-8 |