| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Dimethyl sulfoxide
CAS:67-68-5 |
|
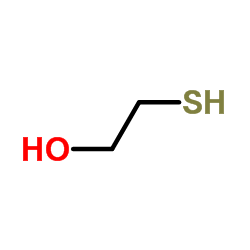 |
mercaptoethanol
CAS:60-24-2 |
|
 |
Magnesium choride
CAS:7786-30-3 |
|
 |
trisodium phosphate
CAS:7601-54-9 |
|
 |
GW9662
CAS:22978-25-2 |
|
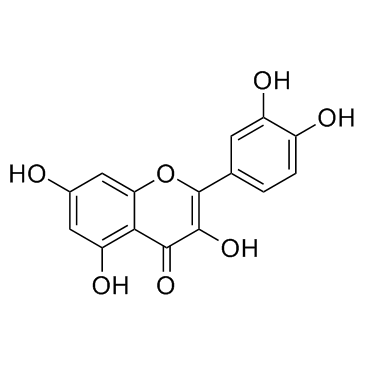 |
Quercetin
CAS:117-39-5 |
|
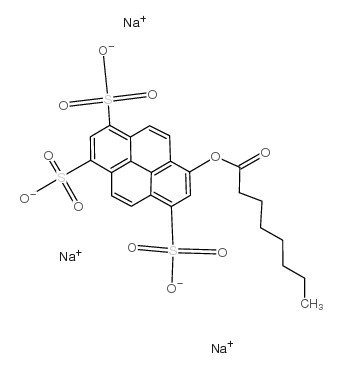 |
8-Octanoyloxypyrene-1,3,6-trisulfonic acid trisodium salt
CAS:115787-84-3 |
|
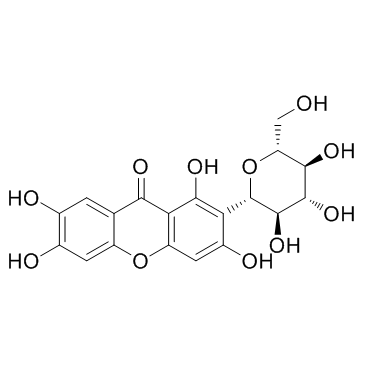 |
Mangiferin
CAS:4773-96-0 |