| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Dimethyl sulfoxide
CAS:67-68-5 |
|
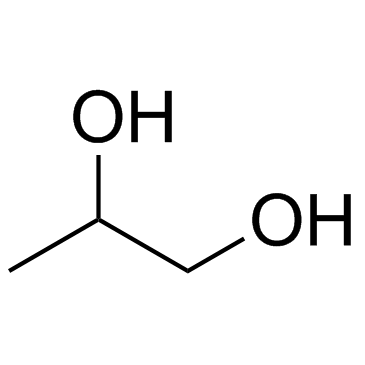 |
Propylene Glycol
CAS:57-55-6 |
|
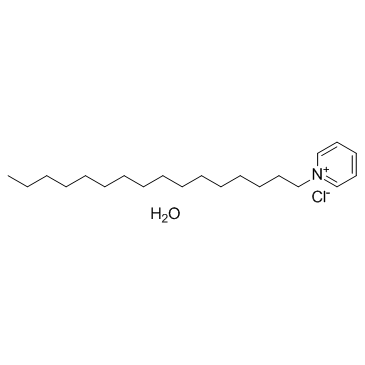 |
Cetylpyridinium chloride monohydrate
CAS:6004-24-6 |
|
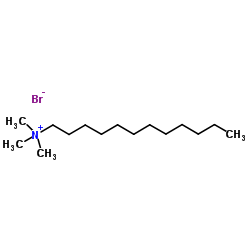 |
DTAB
CAS:1119-94-4 |
|
 |
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
CAS:60-00-4 |
|
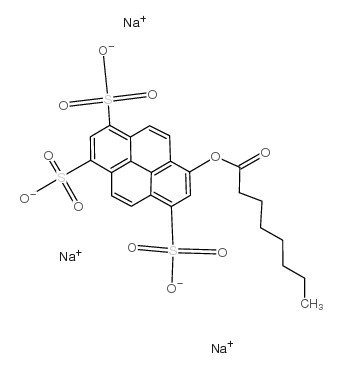 |
8-Octanoyloxypyrene-1,3,6-trisulfonic acid trisodium salt
CAS:115787-84-3 |