2,4-diaminopyrimidine derivatives as potent growth hormone secretagogue receptor antagonists.
Michael D Serby, Hongyu Zhao, Bruce G Szczepankiewicz, Christi Kosogof, Zhili Xin, Bo Liu, Mei Liu, Lissa T J Nelson, Wiweka Kaszubska, H Douglas Falls, Verlyn Schaefer, Eugene N Bush, Robin Shapiro, Brian A Droz, Victoria E Knourek-Segel, Thomas A Fey, Michael E Brune, David W A Beno, Theresa M Turner, Christine A Collins, Peer B Jacobson, Hing L Sham, Gang Liu
Index: J. Med. Chem. 49(8) , 2568-78, (2006)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Ghrelin, a gut-derived orexigenic hormone, is an endogenous ligand of the growth hormone secretagogue receptor (GHS-R). Centrally administered ghrelin has been shown to cause hunger and increase food intake in rodents. Inhibition of ghrelin actions with ghrelin antibody, peptidyl GHS-R antagonists, and antisense oligonucleosides resulted in weight loss and food intake decrease in rodents. Here we report the effects of GHS-R antagonists, some of which were potent, selective, and orally bioavailable. A structure-activity relationship study led to the discovery of 8a, which was effective in decreasing food intake and body weight in several acute rat studies.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
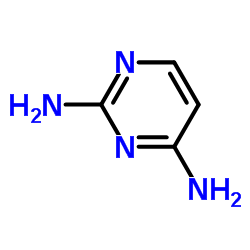 |
2,4-Diaminopyrimidine
CAS:156-81-0 |
C4H6N4 |
|
Contribution of nitric oxide-dependent guanylate cyclase and...
2015-12-01 [Neuropharmacology 99 , 422-31, (2015)] |
|
Design and optimization of hybrid of 2,4-diaminopyrimidine a...
2015-01-01 [Eur. J. Med. Chem. 96 , 269-80, (2015)] |
|
Cocrystals of 6-methyl-2-thiouracil: presence of the accepto...
2015-03-01 [Acta Crystallogr. C Struct. Chem. 71(Pt 3) , 229-38, (2015)] |
|
Ultra performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrom...
2009-03-01 [Anal. Bioanal. Chem 393(6-7) , 1709-18, (2009)] |
|
Inhibitory activities of three classes of acyclic nucleoside...
2007-06-01 [Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 51(6) , 2268-73, (2007)] |