The effects of homologous series of anaesthetics on a resting potassium conductance of the squid giant axon.
A A Elliott, J R Elliott, D A Haydon
Index: Biochim. Biophys. Acta 978(2) , 337-40, (1989)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The effects of n-alkanes (n-pentane to n-octane), n-alkanols (n-pentanol to n-undecanol) and two carboxylic esters (methyl pentanoate and methyl octanoate) on the conductance of squid giant axons in a high potassium, zero sodium bathing solution have been examined. Sodium and delayed rectifier potassium channels were as far as possible pharmacologically blocked. A substantial fraction of the measured conductance is attributed to a recently-described, voltage-independent, potassium channel. Anaesthetics block this channel but its sensitivity is markedly different from those of other squid axon ion channels.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
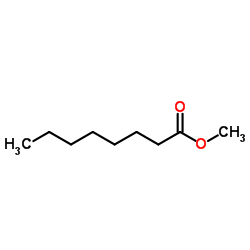 |
Methyl octylate
CAS:111-11-5 |
C9H18O2 |
|
Optimization of supercritical fluid consecutive extractions ...
2015-01-01 [J. Food Sci. 80(1) , E101-7, (2015)] |
|
Use of Commercial Dry Yeast Products Rich in Mannoproteins f...
2015-06-17 [J. Agric. Food Chem. 63 , 5670-81, (2015)] |
|
Evaluation of injection methods for fast, high peak capacity...
2015-05-01 [J. Chromatogr. A. 1392 , 82-90, (2015)] |
|
Gas chromatography with tandem differential mobility spectro...
2015-11-20 [J. Chromatogr. A. 1421 , 162-70, (2015)] |
|
Shared Ligands Between Organic Anion Transporters (OAT1 and ...
2015-12-01 [Drug Metab. Dispos. 43 , 1855-63, (2015)] |