| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
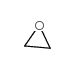 |
ETHYLENE OXIDE
CAS:75-21-8 |
|
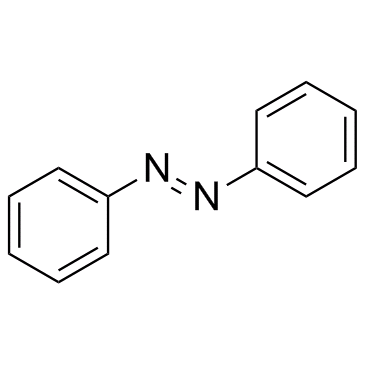 |
Azobenzene
CAS:103-33-3 |