| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
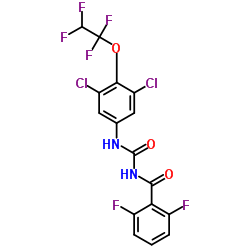 |
Hexaflumuron
CAS:86479-06-3 |
|
 |
Diflubenzuron
CAS:35367-38-5 |