Effects of extracts from Paederia scandens (LOUR.) MERRILL (Rubiaceae) on MSU crystal-induced rats gouty arthritis.
Ying Ma, Lan-Lan Zhou, Hai-Yan Yan, Mei Liu
Index: Am. J. Chin. Med. 37(4) , 669-83, (2009)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The effects of extract of Paederia scandens (LOUR.) MERRILL (Rubiaceae) (EPS), a Chinese traditional herbal medicine, on inflammatory and immune responses and their mechanisms in MSU crystals-induced (GA) rats were studied. GA rats were established. Ankle joint volume of rats was measured by volume meter; the level of TNF-alpha and IL-1beta was determined by radioimmunoassay. mRNA expressions of TNF-alpha and IL-1beta in synovial tissue of GA rats were analyzed by RT-PCR, and the expression of NF-kappaB was detected by immunohistochemistry. The administration of EPS (2.25, 4.5 g/kg, ig 9 days) inhibited the inflammatory response in GA rats. The mRNA expressions of TNF-alpha and IL-1beta were also significantly suppressed in synovial tissue. In addition, EPS (2.25, 4.5 g/kg, ig 9 days) inhibited the expression of TNF-alpha and IL-1beta and the biological activity of NF-kappaB. These results suggested that EPS possesses antiinflammatory effects by modulating pro-inflammatory mediators' production in synovial tissue and inactivating NF-kappaB pathway transmembrane signal transduction which plays a crucial role in the pathogenesis of this disease.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
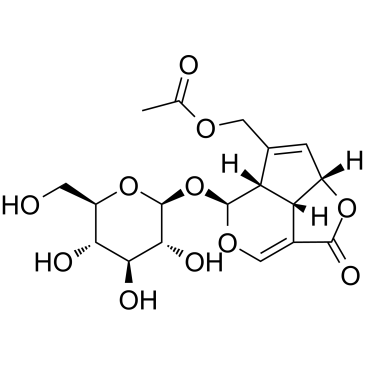 |
Asperuloside
CAS:14259-45-1 |
C18H22O11 |
|
Chemical constituents of the fruits of Morinda citrifolia (N...
2005-04-01 [J. Nat. Prod. 68 , 592-5, (2005)] |
|
[Chemical constituents from root of Lasianthus acuminatissim...
2006-01-01 [Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 31(2) , 133-5, (2006)] |
|
[Isolation and identification of chemical constituents from ...
1992-02-01 [Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 17(2) , 98-100, 127, (1992)] |
|
Novel trisaccharide fatty acid ester identified from the fru...
1999-12-01 [J. Agric. Food Chem. 47(12) , 4880-2, (1999)] |
|
Antimutagenicity of Tochu tea (an aqueous extract of Eucommi...
1997-01-15 [Mutat. Res. 388(1) , 7-20, (1997)] |