| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
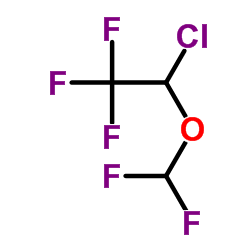 |
Isoflurane
CAS:26675-46-7 |
|
 |
Lidocaine
CAS:137-58-6 |
|
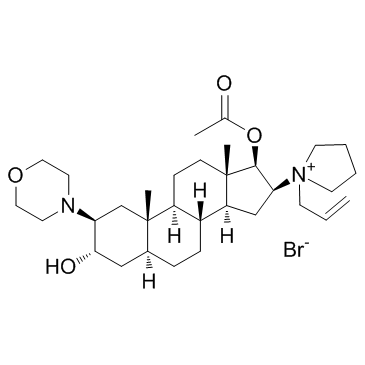 |
Rocuronium bromide
CAS:119302-91-9 |