| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
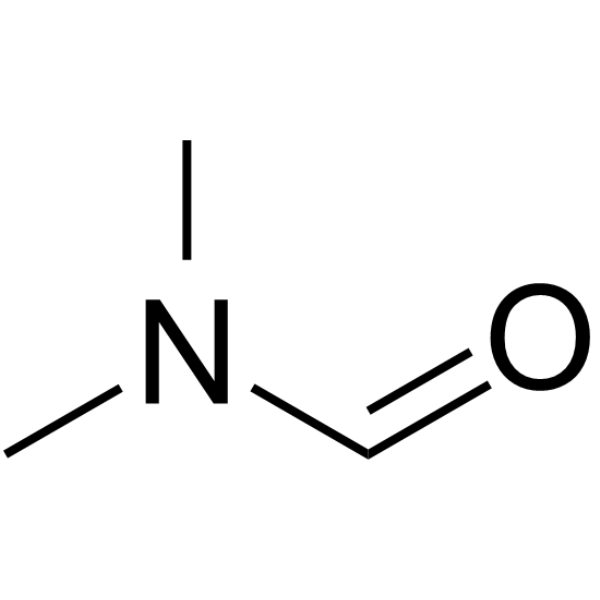 |
N,N-Dimethylformamide
CAS:68-12-2 |
|
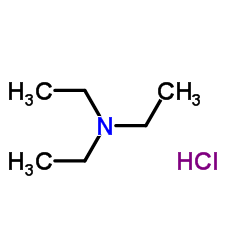 |
Triethylammonium chloride
CAS:554-68-7 |
|
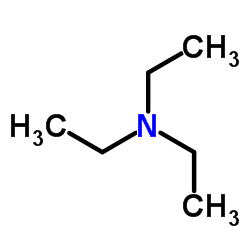 |
Triethylamine
CAS:121-44-8 |
|
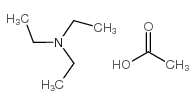 |
triethylammonium acetate
CAS:5204-74-0 |
|
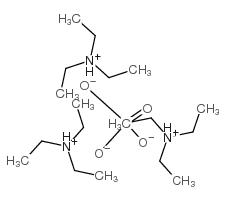 |
Triethylamine Phosphate
CAS:35365-94-7 |
|
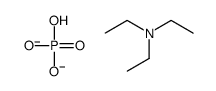 |
triethylammonium phosphate
CAS:10138-93-9 |