| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
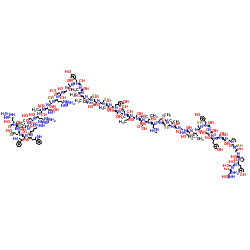 |
Epidermal Growth Factor (from mouse)
CAS:62229-50-9 |
|
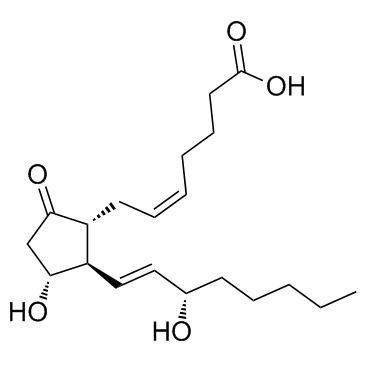 |
Dinoprostone
CAS:363-24-6 |
|
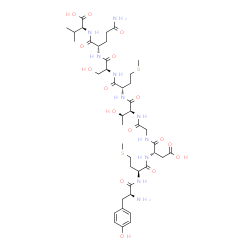 |
TYROSINASE
CAS:9002-10-2 |