| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
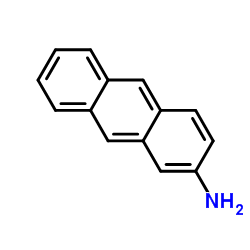 |
2-Anthracenamine
CAS:613-13-8 |
|
 |
Poly(vinylsulfonic acid, sodium salt) solution
CAS:9002-97-5 |