Yeast polysaccharide affects fusaric acid content in maize root rot.
Antónia Srobárová, Grigorij Kogan, Stefan Eged
Index: Chem. Biodivers. 2(12) , 1685-90, (2005)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Protective action of sulfoethyl glucan (SEG), a derivative of the cell wall glucan prepared from the baker's yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, was investigated in the maize seedlings infected by a plant pathogen Fusarium verticillioides (Sacc.). Several markers were assayed with the SEG addition and in the control experiments. Two evaluations were performed on the 7th and the 14th days. Addition of SEG led to the increased productivity parameters of the infected plants and maintained them at the level of non-infected plants during the 14 days of experiment. After seven days of cultivation, concentration of fusaric acid (=5-butylpyridine-2-carboxylic acid; FA) decreased in all infected plants cultivated in the presence of SEG when compared to that detected in the infected plants grown in the absence of SEG. After 14 days of cultivation, polysaccharide addition resulted in the reduction of FA concentration almost to 75% in comparison to the infected plants grown without polysaccharide addition. In the experiment, when exogenous FA was added to the growth medium, its concentration decreased up to 60% in the presence of SEG. Thus, it is feasible to assume that SEG binds and adsorbs FA, and, in this way, reduces its content and exerts protective action in plants against its toxic effect.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
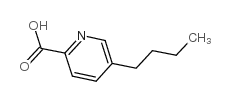 |
Fusaric acid
CAS:536-69-6 |
C10H13NO2 |
|
Characterization of TolC efflux pump proteins from Pasteurel...
2008-11-01 [Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 52 , 4166-71, (2008)] |
|
Chemical genetics reveals a complex functional ground state ...
2007-05-01 [Nat. Chem. Biol. 3(5) , 268-273, (2007)] |
|
Identifying chelators for metalloprotein inhibitors using a ...
2011-01-27 [J. Med. Chem. 54 , 591-602, (2011)] |
|
Determination of the Mycotoxin Content in Distiller's Dried ...
2015-11-04 [J. Agric. Food Chem. 63 , 9441-51, (2015)] |
|
Fusaric acid induces a notochord malformation in zebrafish v...
2015-08-01 [Biometals 28 , 783-9, (2015)] |