| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
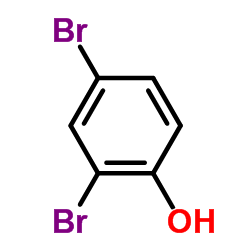 |
2,4-Dibromophenol
CAS:615-58-7 |
|
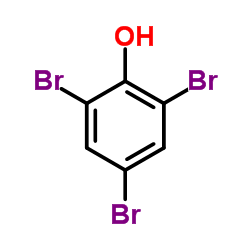 |
2,4,6-Tribromophenol
CAS:118-79-6 |
|
 |
2,6-Dibromophenol
CAS:608-33-3 |
|
 |
4-Bromophenol
CAS:106-41-2 |
|
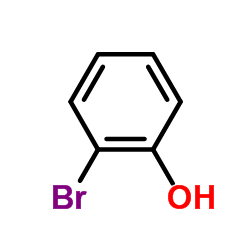 |
2-Bromophenol
CAS:95-56-7 |