A Flow-Cytometry-Based Approach to Facilitate Quantification, Size Estimation and Characterization of Sub-visible Particles in Protein Solutions.
Christian Lubich, Mantas Malisauskas, Thomas Prenninger, Thomas Wurz, Peter Matthiessen, Peter L Turecek, Friedrich Scheiflinger, Birgit M Reipert
Index: Pharm. Res. 32 , 2863-76, (2015)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Sub-visible particles were shown to facilitate unwanted immunogenicity of protein therapeutics. To understand the root cause of this phenomenon, a comprehensive analysis of these particles is required. We aimed at establishing a flow-cytometry-based technology to analyze the amount, size distribution and nature of sub-visible particles in protein solutions.We adjusted the settings of a BD FACS Canto II by tuning the forward scatter and the side scatter detectors and by using size calibration beads to facilitate the analysis of particles with sizes below 1 μM. We applied a combination of Bis-ANS (4,4'-dianilino-1,1'-binaphthyl-5,5'-disulfonic acid dipotassium salt) and DCVJ (9-(2,2-dicyanovinyl)julolidine) to identify specific characteristics of sub-visible particles.The FACS technology allows the analysis of particles between 0.75 and 10 μm in size, requiring relatively small sample volumes. Protein containing particles can be distinguished from non-protein particles and cross-β-sheet structures contained in protein particles can be identified.The FACS technology provides robust and reproducible results with respect to number, size distribution and specific characteristics of sub-visible particles between 0.75 and 10 μm in size. Our data for number and size distribution of particles is in good agreement with results obtained with the state-of-the-art technology micro-flow imaging.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
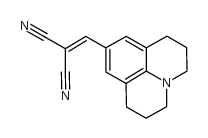 |
9-(2,2-Dicyanovinyl)julolidine
CAS:58293-56-4 |
C16H15N3 |
|
Fluorescent molecular rotors: a new class of probes for tubu...
1989-08-08 [Biochemistry 28 , 6678, (1989)] |
|
9-(Dicyanovinyl)julolidine binding to bovine brain calmoduli...
1991-04-01 [J. Biochem. 109 , 499, (1991)] |
|
Antibodies for fluorescent molecular rotors.
1993-07-27 [Biochemistry 32 , 7589, (1993)] |
|
Conformational Dynamics of Specific Aβ Oligomers Govern Thei...
2016-04-19 [Biochemistry 55 , 2238-50, (2016)] |
|
Characterization and Higher-Order Structure Assessment of an...
2016-03-16 [Bioconjug. Chem. 27 , 604-15, (2016)] |