| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
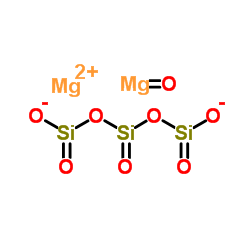 |
MAGNESIUM TRISILICATE
CAS:14987-04-3 |
|
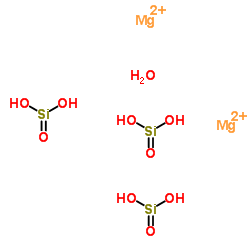 |
Sepiolite powder
CAS:63800-37-3 |