Mosquito larvicidal activity of active constituent derived from Chamaecyparis obtusa leaves against 3 mosquito species.
Young-Su Jang, Ju-Hyun Jeon, Hoi-Seon Lee
Index: J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc. 21(4) , 400-3, (2005)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Mosqutio larvicidal activity of Chamaecyparis obtusa leaf-derived materials against the 4th-stage larvae of Aedes aegypti (L.), Ochlerotatus togoi (Theobald), and Culex pipiens pallens (Coquillett) was examined in the laboratory. A crude methanol extract of C. obtusa leaves was found to be active (percent mortality rough) against the 3 species larvae; the hexane fraction of the methanol extract showed a strong larvicidal activity (100% mortality) at 100 ppm. The bioactive component in the C. obtusa leaf extract was characterized as beta-thujaplicin by spectroscopic analyses. The LC50 value of beta-thujaplicin was 2.91, 2.60, and 1.33 ppm against Ae. aegypti, Oc. togoi, and Cx. pipiens pallens larvae. This naturally occurring C. obtusa leaves-derived compound merits further study as a potential mosquito larval control agent or lead compound.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
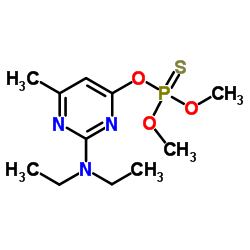 |
Pirimiphos-methyl
CAS:29232-93-7 |
C11H20N3O3PS |
|
Erythropoietic response and hematological parameters in the ...
2005-11-01 [Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 62(3) , 436-40, (2005)] |
|
Evaluation of immunotoxicity induced by pirimiphos-methyl in...
2007-08-01 [J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 70(15-16) , 1278-87, (2007)] |
|
Effects of individual and binary-combined commercial insecti...
2013-09-01 [Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 36(2) , 715-23, (2013)] |
|
Heterogeneous reactions of pirimiphos-methyl and pirimicarb ...
2012-11-08 [J. Phys. Chem. A 116(44) , 10802-9, (2012)] |
|
A preliminary investigation of insect colonization and succe...
2011-01-01 [Forensic Sci. Int. 208(1-3) , e26-30, (2011)] |