Chromatographic determination of cyanoglycosides prunasin and amygdalin in plant extracts using a porous graphitic carbon column.
V Berenguer-Navarro, R M Giner-Galván, N Grané-Teruel, G Arrazola-Paternina
Index: J. Agric. Food Chem. 50(24) , 6960-3, (2002)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The determination of cyanogenic compounds in plants is often performed by HPLC. However, in this analysis, interferences due to compounds in the matrix, such as tannins and other pigments, are encountered, especially in roots and leaves. A new method is proposed for determining the cyanogenic glycosides amygdalin (D-mandelonitrile beta-D-gentiobioside) and prunasin (D-mandelonitrile beta-D-glucoside) in almond tree tissues, using poly(vinylpyrrolidone) or active carbon as scavengers for extracting cyanogenic compounds from roots or leaves, respectively. A new chromatographic approach for conducting the analysis is also discussed herein. The advantages of a Hypercarb column for the analysis of prunasin in roots are shown. The correlation coefficient with a reference method is high (>0.99), and statistical tests prove that the two methods are equivalent. In addition, the results provide evidence that prunasin is the only cyanoglycoside present in almond tree roots.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
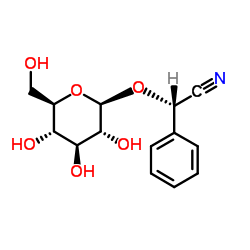 |
Prunasin
CAS:99-18-3 |
C14H17NO6 |
|
Larvae of the fall webworm, Hyphantria cunea, inhibit cyanog...
2008-03-01 [J. Immunol. Methods 211 , 671-7, (2008)] |
|
Generation of primary amide glucosides from cyanogenic gluco...
2009-01-01 [Phytochemistry 70(3) , 388-93, (2009)] |
|
Natural glycosides containing allopyranose from the passion ...
2001-07-12 [Org. Lett. 3(14) , 2193-5, (2001)] |
|
Characterisation of galloylated cyanogenic glucosides and hy...
2011-01-01 [Phytochem. Anal. 22(6) , 516-25, (2011)] |
|
Cloning, sequencing, and characterization of a membrane-asso...
1995-10-01 [J. Bacteriol. 177(20) , 5884-90, (1995)] |