| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
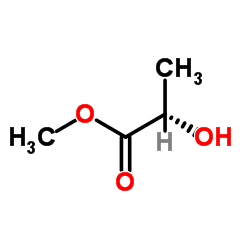 |
(−)-Methyl L-lactate
CAS:27871-49-4 |
|
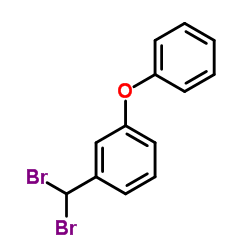 |
1-(Dibromomethyl)-3-phenoxybenzene
CAS:547-64-8 |
|
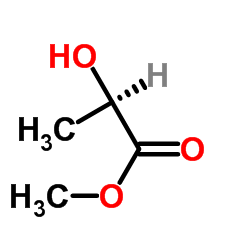 |
Methyl-D-(+)-Lactate
CAS:17392-83-5 |