| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
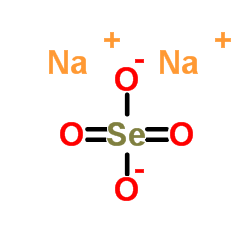 |
sodium selenate
CAS:13410-01-0 |
|
 |
Sodium selenate decahydrate
CAS:10102-23-5 |