| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
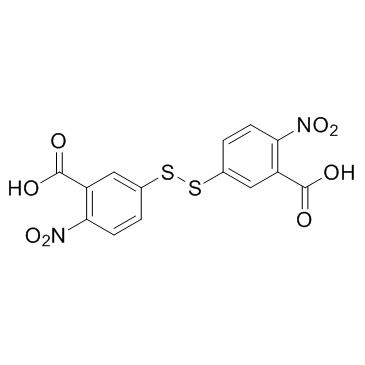 |
DTNB
CAS:69-78-3 |
|
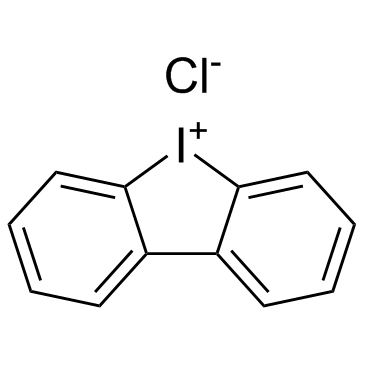 |
Diphenyleneiodonium chloride
CAS:4673-26-1 |
|
 |
2,2′-dithiodibenzoic acid
CAS:119-80-2 |