| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
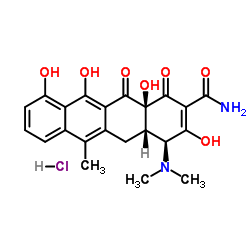 |
Anhydrotetracycline Hydrochloride
CAS:13803-65-1 |
|
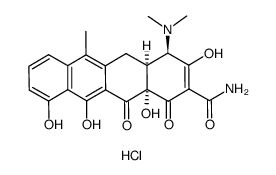 |
4-Epianhydrotetracycline hydrochloride
CAS:4465-65-0 |