Canadian journal of biochemistry
1979-10-01
N-acylation of tyramines: purification and characterization of an arylamine N-acetyltransferase from rat brain and liver.
P H Yu, A A Boulton
Index: Can. J. Biochem. 57(10) , 1204-9, (1979)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The N-acylation of tyramine isomers and other biogenic amines has been studied. The liver exhibits the highest activity towards tyramines, while the brain exhibits a low but significant activity. In the brain, tyramine N-acylation activity was heterogenously distributed. The arylamine N-acetyltransferase has been partially purified from both rat liver and brain, the two enzymes being quite similar with respect to their chromatographic properties, optimal pH requirement (pH 7.8), and their kinetic parameters. The product N-acetyltyramine is not oxidized by liver amidohydrolase or monoamine oxidase.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
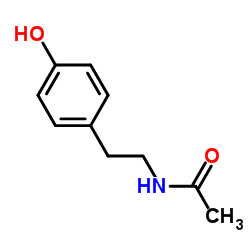 |
N-Acetyltyramine
CAS:1202-66-0 |
C10H13NO2 |
Related Articles:
More...
|
Selective nanomolar detection of dopamine using a boron-dope...
2009-05-15 [Anal. Chem. 81(10) , 4089-98, (2009)] |
|
Mechanistic and structural analysis of Drosophila melanogast...
2014-12-16 [Biochemistry 53(49) , 7777-93, (2014)] |
|
Effect of acetyl derivatives of some sympathomimetic amines ...
1977-02-01 [Acta Pharmacol. Toxicol. (Copenh.) 40(2) , 247-58, (1977)] |
|
Partial purification and properties of N-acetylhistamine dea...
1976-07-08 [Biochim. Biophys. Acta 438(2) , 532-9, (1976)] |
|
Effect of spores of saprophytic fungi on phytoalexin accumul...
2000-08-01 [J. Agric. Food Chem. 48(8) , 3662-5, (2000)] |