| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
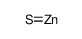 |
Zinc sulfide
CAS:1314-98-3 |
|
 |
Tellurium
CAS:13494-80-9 |
|
 |
Cadmium telluride
CAS:1306-25-8 |