| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Ascorbic acid
CAS:50-81-7 |
|
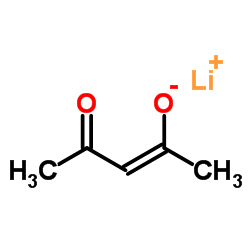 |
Lithium (2Z)-4-oxo-2-penten-2-olate
CAS:18115-70-3 |
|
 |
Nickel Chloride
CAS:7718-54-9 |
|
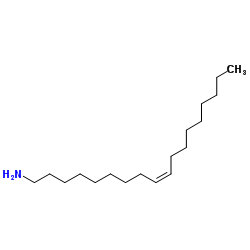 |
Oleylamine
CAS:112-90-3 |