| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Formaldehyde
CAS:50-00-0 |
|
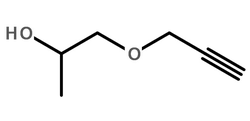 |
Native Sweet Potato Non-Prostatic Acid Phosphatase
CAS:9001-77-8 |
|
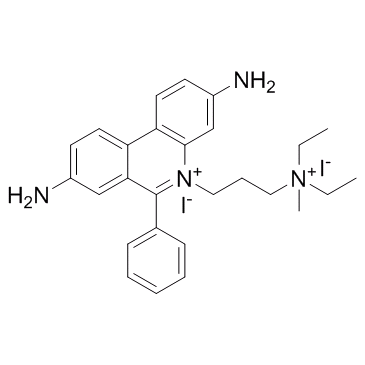 |
Propidium Iodide
CAS:25535-16-4 |
|
 |
HUMAN M-CSF
CAS:81627-83-0 |