The natural product cucurbitacin E inhibits depolymerization of actin filaments.
Pia M Sörensen, Roxana E Iacob, Marco Fritzsche, John R Engen, William M Brieher, Guillaume Charras, Ulrike S Eggert
Index: ACS Chem. Biol. 7 , 1502-1508, (2012)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Although small molecule actin modulators have been widely used as research tools, only one cell-permeable small molecule inhibitor of actin depolymerization (jasplakinolide) is commercially available. We report that the natural product cucurbitacin E inhibits actin depolymerization and show that its mechanism of action is different from jasplakinolide. In assays using pure fluorescently labeled actin, cucurbitacin E specifically affects depolymerization without affecting polymerization. It inhibits actin depolymerization at substoichiometric concentrations up to 1:6 cucurbitacin E:actin. Cucurbitacin E specifically binds to filamentous actin (F-actin) forming a covalent bond at residue Cys257, but not to monomeric actin (G-actin). On the basis of its compatibility with phalloidin staining, we show that cucurbitacin E occupies a different binding site on actin filaments. Using loss of fluorescence after localized photoactivation, we found that cucurbitacin E inhibits actin depolymerization in live cells. Cucurbitacin E is a widely available plant-derived natural product, making it a useful tool to study actin dynamics in cells and actin-based processes such as cytokinesis.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
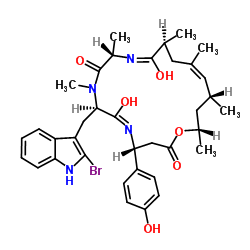 |
Jasplakinolide
CAS:102396-24-7 |
C36H45BrN4O6 |
|
Rapid changes in phospho-MAP/tau epitopes during neuronal st...
2011-01-01 [PLoS ONE 6 , e20878, (2011)] |
|
P2Y2 receptor signaling in neutrophils is regulated from ins...
2015-08-15 [Exp. Cell Res. 336 , 242-52, (2015)] |
|
Actin polymerization controls the activation of multidrug ef...
2012-09-01 [Mol. Biol. Cell 23(18) , 3663-72, (2012)] |
|
F-actin-myosin II inhibitors affect chromaffin granule plasm...
2012-10-01 [J. Mol. Neurosci. 48(2) , 328-38, (2012)] |
|
Endothelial actin depolymerization mediates NADPH oxidase-su...
2014-01-01 [Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 306(1) , H69-77, (2014)] |