| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
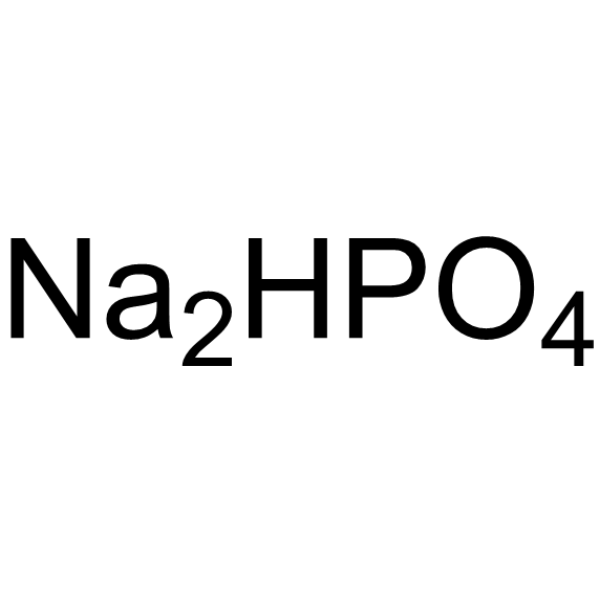 |
Disodium hydrogenorthophosphate
CAS:7558-79-4 |
|
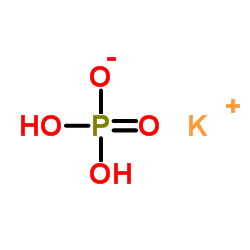 |
Monopotassium phosphate
CAS:7778-77-0 |
|
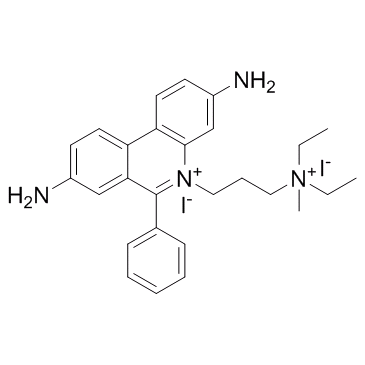 |
Propidium Iodide
CAS:25535-16-4 |
|
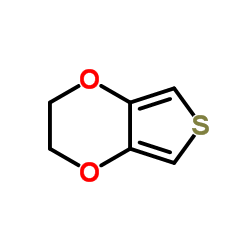 |
3,4-Ethylenedioxythiophene
CAS:126213-50-1 |