| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Dimethylamine hydrochloride
CAS:506-59-2 |
|
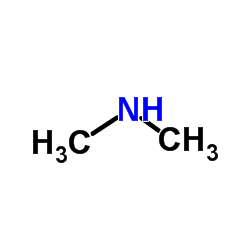 |
Dimethylamine
CAS:124-40-3 |
|
 |
Trimethylamine
CAS:75-50-3 |
|
 |
Trimethylammonium monohydrochloride
CAS:593-81-7 |