| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
sodium dodecyl sulfate
CAS:151-21-3 |
|
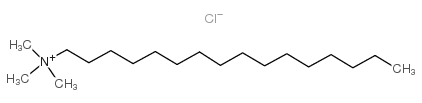 |
N-Hexadecyltrimethylammonium chloride
CAS:112-02-7 |
|
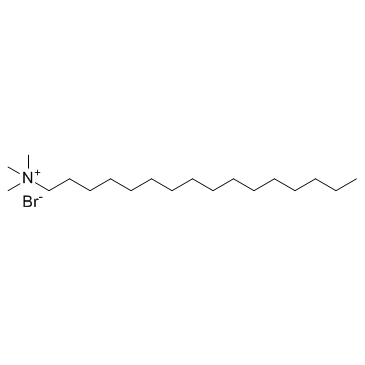 |
Hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide
CAS:57-09-0 |
|
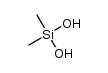 |
Silicone oil
CAS:63148-62-9 |
|
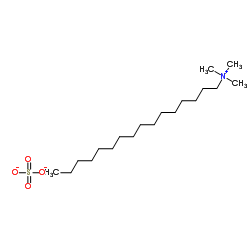 |
hexadecyl-trimethyl-ammonium sulfate
CAS:68214-07-3 |