| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Methanol
CAS:67-56-1 |
|
 |
L-(+)-Lysine monohydrochloride
CAS:657-27-2 |
|
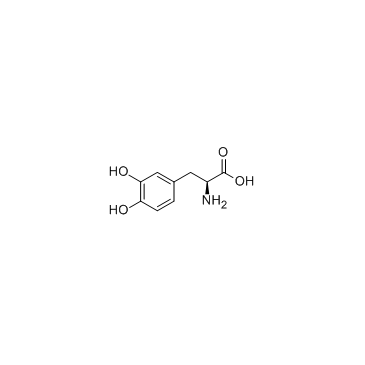 |
Levodopa
CAS:59-92-7 |
|
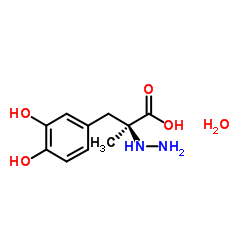 |
Carbidopa monohydrate
CAS:38821-49-7 |
|
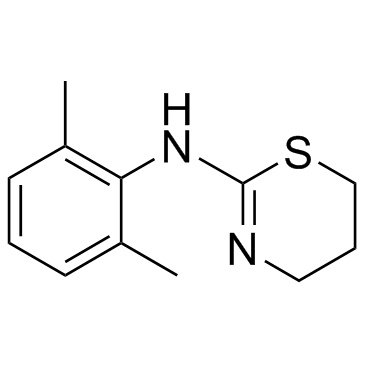 |
Xylazine
CAS:7361-61-7 |
|
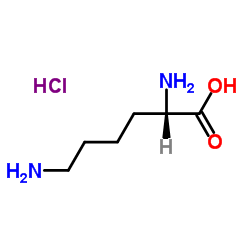 |
L-Lysine hydrochloride
CAS:10098-89-2 |
|
 |
L-3,4-Dihydroxyphenylalanine Methyl ester hydrochloride
CAS:1421-65-4 |