| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
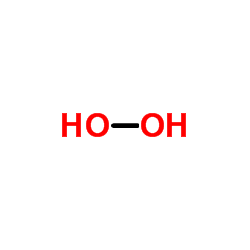 |
Hydrogen peroxide
CAS:7722-84-1 |
|
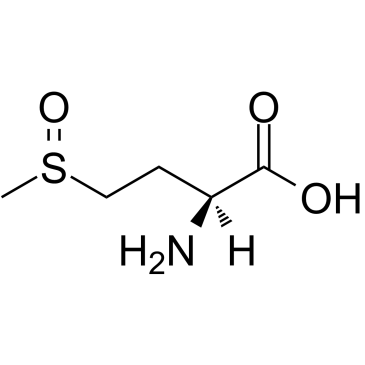 |
H-Met(O)-OH
CAS:3226-65-1 |