| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
3-Fluoro-DL-phenylalanine
CAS:456-88-2 |
|
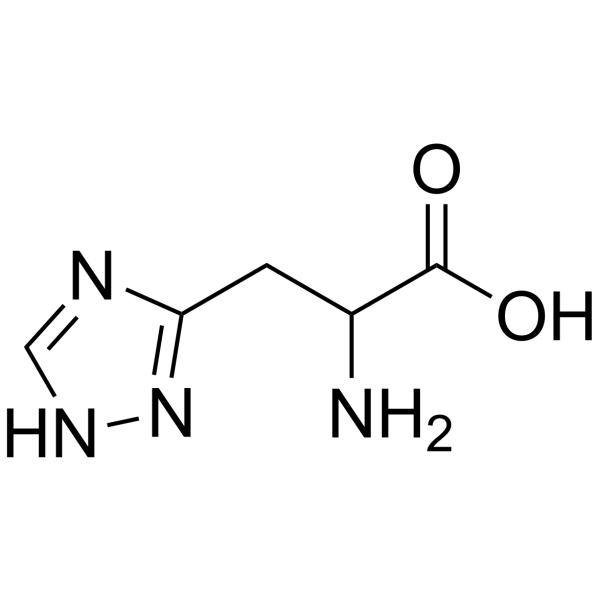 |
1H-1,2,4-Triazole-5-propanoicacid, a-amino
CAS:10109-05-4 |
|
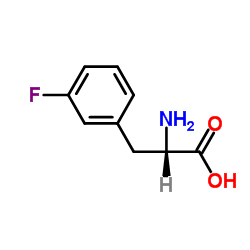 |
3-Fluorophenylalanine
CAS:19883-77-3 |
|
 |
2-Fluorophenylalanine
CAS:2629-55-2 |