Biosynthesis of the irregular monoterpene artemisia ketone, the sesquiterpene germacrene D and other isoprenoids in Tanacetum vulgare L. (Asteraceae).
Dirk Umlauf, Josef Zapp, Hans Becker, Klaus Peter Adam
Index: Phytochemistry 65(17) , 2463-70, (2004)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The incorporation of [1-13C]-labeled glucose into the irregular monoterpene artemisia ketone, the regular monoterpenes camphor and beta-thujone, the sesquiterpene germacrene D, the diterpene trans-phytol and beta-sitosterol and isofucosterol has been studied in axenic cultures of Tanacetum vulgare L. (Asteraceae). Quantitative 13C NMR spectroscopic analysis of the resulting labeling patterns showed that the isoprene units of the monoterpenes and the diterpene are formed via the methylerythritol phosphate (MEP) pathway, whereas the isoprene building blocks of the sesquiterpene and the sterols originate from the mevalonic acid (MVA) pathway.Copyright 2004 Elsevier Ltd.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
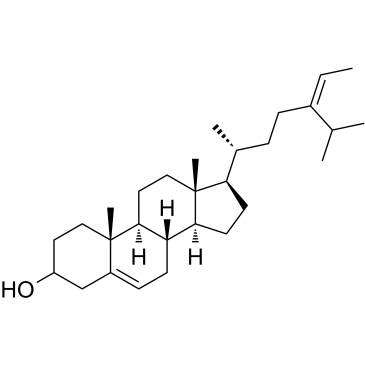 |
Fucosterol
CAS:17605-67-3 |
C29H48O |
|
Kinetics and molecular docking studies of an anti-diabetic c...
2013-10-25 [Chem. Biol. Interact. 206(1) , 55-62, (2013)] |
|
The effect of traditional stir-frying process on hydrophilic...
2015-01-01 [Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 66 , 873-80, (2015)] |
|
Inhibition of Mycobacterium tuberculosis growth by saringost...
2001-11-01 [J. Nat. Prod. 64(11) , 1463-4, (2001)] |
|
Visible fibrinolysis by endothelial cells: effect of vitamin...
1986-12-01 [Biosci. Rep. 6(12) , 1029-33, (1986)] |
|
Isolation of two new C30 sterols, (24E)-24-N-propylidenechol...
1980-02-01 [Steroids 35(2) , 219-31, (1980)] |