| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
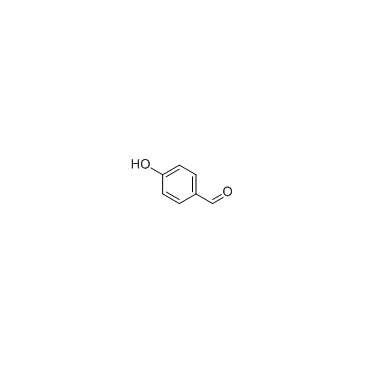 |
4-hydroxybenzaldehyde
CAS:123-08-0 |
|
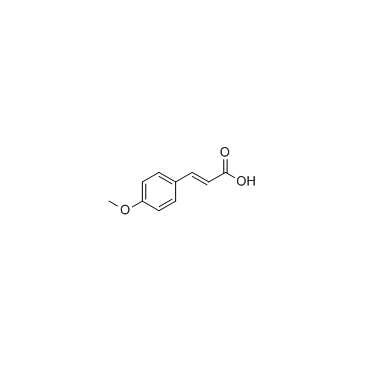 |
4-Methoxycinnamic acid
CAS:830-09-1 |
|
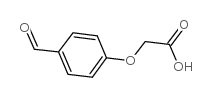 |
4-Formylphenoxyacetic acid
CAS:22042-71-3 |