| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
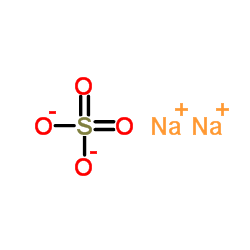 |
sodium sulfate
CAS:7757-82-6 |
|
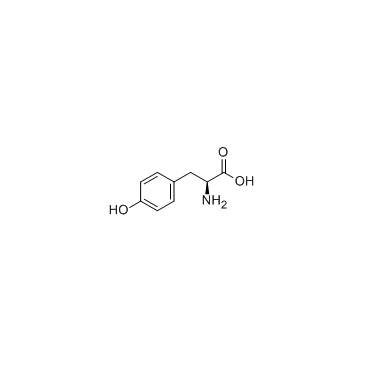 |
L-Tyrosine
CAS:60-18-4 |
|
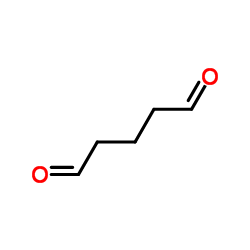 |
glutaraldehyde
CAS:111-30-8 |
|
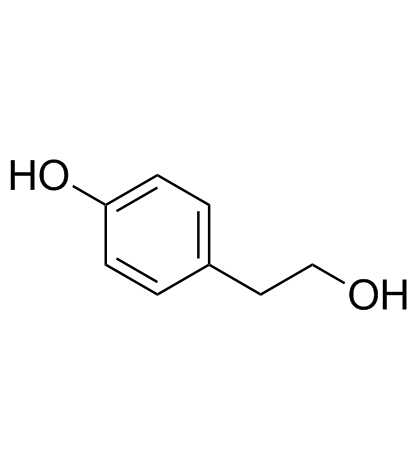 |
4-Hydroxyphenyl ethanol
CAS:501-94-0 |
|
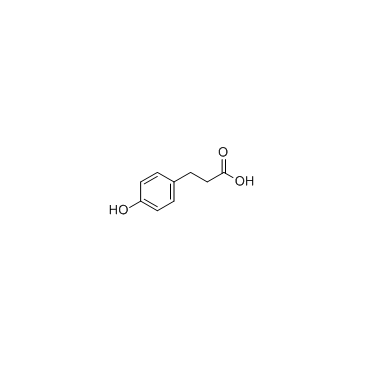 |
Desaminotyrosine
CAS:501-97-3 |