| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Acetonitrile
CAS:75-05-8 |
|
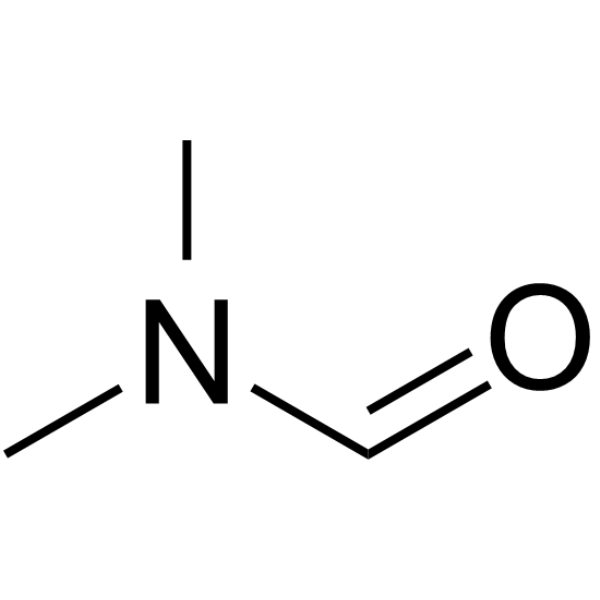 |
N,N-Dimethylformamide
CAS:68-12-2 |
|
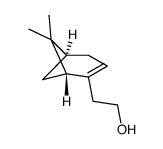 |
(-)-NOPOL
CAS:35836-73-8 |
|
 |
Potassium hexafluorophosphate
CAS:17084-13-8 |
|
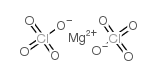 |
Magnesium perchlorate
CAS:10034-81-8 |