| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
etbe
CAS:637-92-3 |
|
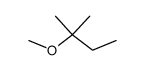 |
tert-Amyl methyl ether
CAS:994-05-8 |