| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
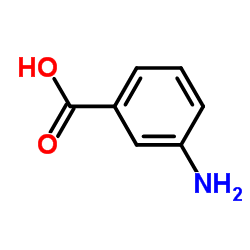 |
3-Aminobenzoic acid
CAS:99-05-8 |
|
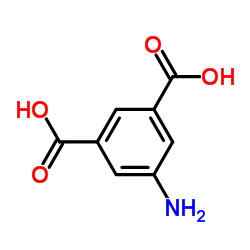 |
5-Aminoisophthalic acid
CAS:99-31-0 |
|
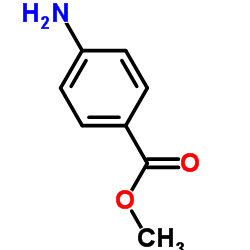 |
Methyl 4-aminobenzoate
CAS:619-45-4 |
|
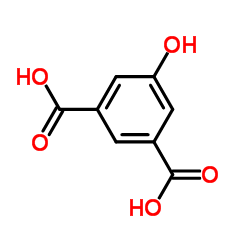 |
5-Hydroxyisophthalic acid
CAS:618-83-7 |