| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
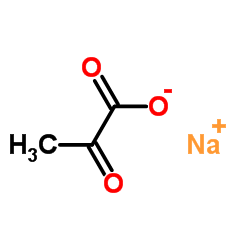 |
Sodium 2-oxopropanoate
CAS:113-24-6 |
|
 |
HEPES
CAS:7365-45-9 |
|
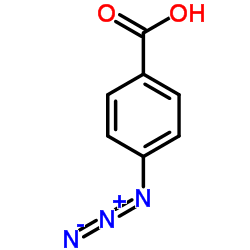 |
4-Azidobenzoic acid
CAS:6427-66-3 |