| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
4-aminosalicylic acid
CAS:65-49-6 |
|
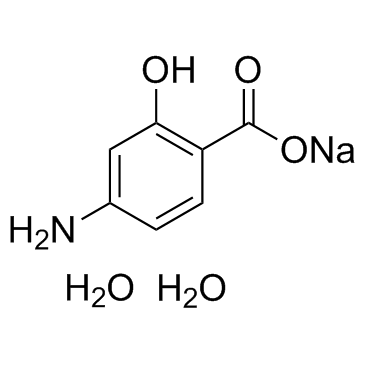 |
Sodium 4-aminosalicylate dihydrate
CAS:6018-19-5 |
|
 |
Ethionamide
CAS:536-33-4 |