| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
N-hexane
CAS:110-54-3 |
|
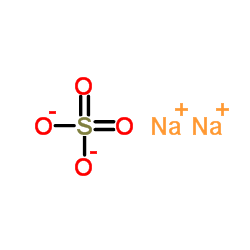 |
sodium sulfate
CAS:7757-82-6 |
|
 |
Dichloromethane
CAS:75-09-2 |
|
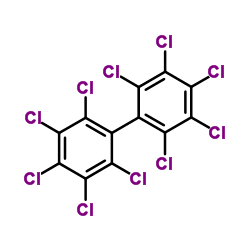 |
Decachlorobiphenyl
CAS:2051-24-3 |