| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
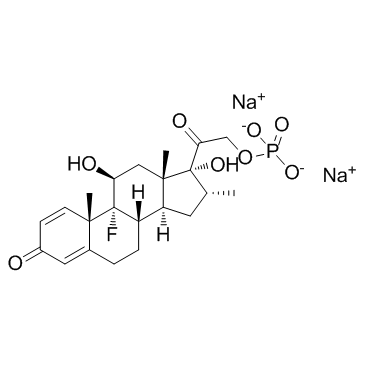 |
Dexamethasone 21-phosphate disodium salt
CAS:2392-39-4 |
|
 |
Dexamethasone-17-acetate
CAS:1177-87-3 |