Excretion profile of corticosteroids in bovine urine compared with tissue residues after therapeutic and growth-promoting administration of dexamethasone.
Carolina Ferranti, Marco Famele, Luca Palleschi, Elena Bozzetta, Marzia Pezzolato, Rosa Draisci
Index: Steroids 78(9) , 803-12, (2013)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The illicit use of dexamethasone as growth-promoting agent in animal breeding is still practiced within the EU constituting a health risk for meat consumers. An experimental study was developed to assess dexamethasone urinary excretion and tissue distribution (liver, kidney, and muscle) in male calves after therapeutic and growth-promoting administration. Urine and tissue samples collected from treated and untreated bovines were also investigated for the presence of other natural and synthetic corticosteroids (prednisolone, prednisone, hydrocortisone, and cortisone), in order to study a possible correlation with dexamethasone administration and to clarify prednisolone origin. Analyses were performed by a multi-residue LC-MS/MS method developed and validated according to the Commission Decision 2002/657/EC. The results confirm the rapid rate of dexamethasone urinary excretion, irrespective of the dosage, the duration and the route of administration, and the disappearance of cortisone and hydrocortisone during the treatment. Dexamethasone was distributed to the tissues where the elimination rate proceeded relatively slower as suggested by the presence of residues one month after the withdrawal of the therapeutic treatment. An increase in the number of positive findings for prednisolone, in association with higher levels of cortisone and hydrocortisone, was observed in urine samples collected from slaughterhouse rather than those collected at the farm. Prednisone residues were found only in one urine sample that showed the highest levels of prednisolone, hydrocortisone, and cortisone. The occurrence of prednisolone residues in urine and even in tissue samples confirms the endogenous nature of this molecule. Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
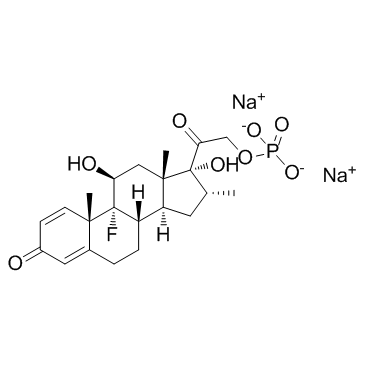 |
Dexamethasone 21-phosphate disodium salt
CAS:2392-39-4 |
C22H28FNa2O8P |
|
Developmental Expression and Glucocorticoid Control of the L...
2015-01-01 [PLoS ONE 10 , e0136115, (2015)] |
|
Contralateral eye comparison of descemet membrane endothelia...
2015-01-01 [Am. J. Ophthalmol. 159(1) , 155-9.e1, (2014)] |
|
Eliminating antibiotic prophylaxis for intravitreal injectio...
2015-04-01 [Retina (Philadelphia, Pa.) 35(4) , 783-8, (2015)] |
|
The AKT signaling pathway sustains the osteogenic differenti...
2015-08-01 [Mol. Cell Biochem. 406 , 199-204, (2015)] |
|
Subchronic glucocorticoid receptor inhibition rescues early ...
[Neuropsychopharmacology 40 , 1772-81, (2015)] |