| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
n-tert-butyldiethanolamine
CAS:2160-93-2 |
|
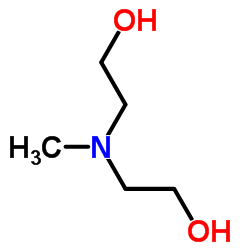 |
N-Methyldiethanolamine
CAS:105-59-9 |