| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
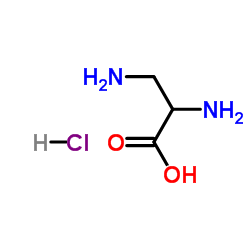 |
UNII:IU6ICR549L
CAS:54897-59-5 |
|
 |
3-Amino-L-alanine hydrochloride
CAS:1482-97-9 |