| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Poly(oxy-1,4-phenylenesulfonyl-1,4-phenylene)
CAS:25608-63-3 |
|
 |
Cupric chloride
CAS:7447-39-4 |
|
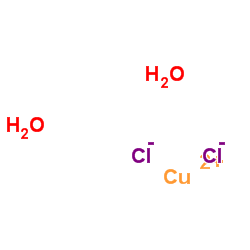 |
Copper(II) chloride dihydrate
CAS:10125-13-0 |