| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Sodium alginate
CAS:9005-38-3 |
|
 |
agarose
CAS:9012-36-6 |
|
 |
Cesium
CAS:7440-46-2 |
|
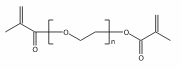 |
Poly(ethylene glycol) dimethacrylate
CAS:25852-47-5 |
|
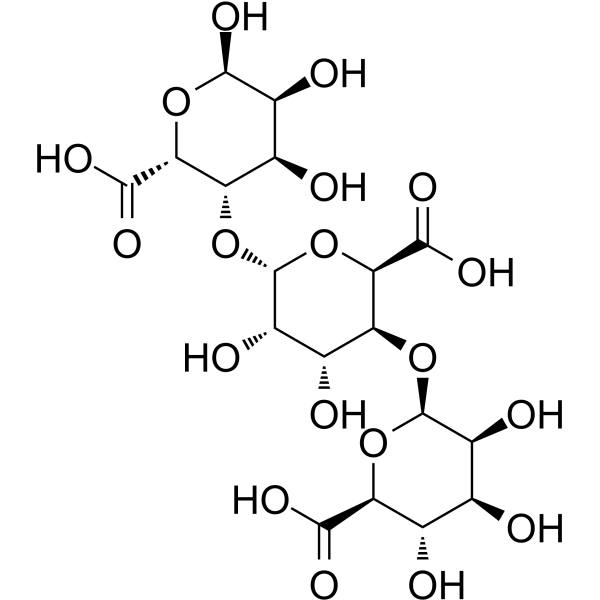 |
β-D-Mannopyranuronic acid
CAS:9005-32-7 |
|
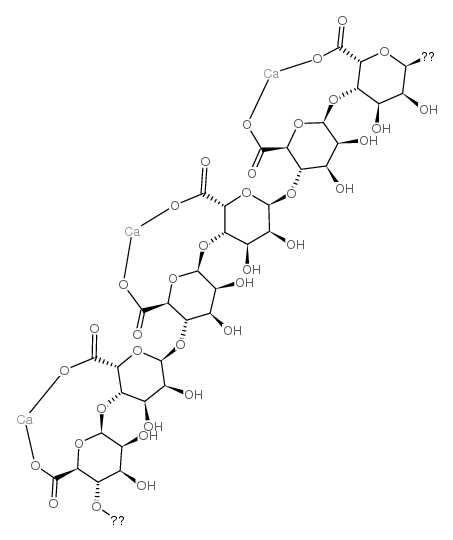 |
Calcium alginate
CAS:9005-35-0 |