Hydrogen-rich saline improves survival and neurological outcome after cardiac arrest and cardiopulmonary resuscitation in rats.
Ting-ting Huo, Yi Zeng, Xiao-nan Liu, Li Sun, Huan-zhi Han, Hong-guang Chen, Zhi-hong Lu, Yi Huang, Huang Nie, Hai-long Dong, Ke-liang Xie, Li-ze Xiong
Index: Anesth. Analg. 119(2) , 368-80, (2014)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Sudden cardiac arrest is a leading cause of death worldwide. Three-fourths of cardiac arrest patients die before hospital discharge or experience significant neurological damage. Hydrogen-rich saline, a portable, easily administered, and safe means of delivering hydrogen gas, can exert organ-protective effects through regulating oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis. We designed this study to investigate whether hydrogen-rich saline treatment could improve survival and neurological outcome after cardiac arrest and cardiopulmonary resuscitation, and the mechanism responsible for this effect.Sprague-Dawley rats were subjected to 8 minutes of cardiac arrest by asphyxia. Different doses of hydrogen-rich saline or normal saline were administered IV at 1 minute before cardiopulmonary resuscitation, followed by injections at 6 and 12 hours after restoration of spontaneous circulation, respectively. We assessed survival, neurological outcome, oxidative stress, inflammation biomarkers, and apoptosis.Hydrogen-rich saline treatment dose dependently improved survival and neurological function after cardiac arrest/resuscitation. Moreover, hydrogen-rich saline treatment dose dependently ameliorated brain injury after cardiac arrest/resuscitation, which was characterized by the increase of survival neurons in hippocampus CA1, reduction of brain edema in cortex and hippocampus, preservation of blood-brain barrier integrity, as well as the decrease of serum S100β and neuron-specific enolase. Furthermore, we found that the beneficial effects of hydrogen-rich saline treatment were associated with decreased levels of oxidative products (8-iso-prostaglandin F2α and malondialdehyde) and inflammatory cytokines (tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-1β, and high-mobility group box protein 1), as well as the increased activity of antioxidant enzymes (superoxide dismutase and catalase) in serum and brain tissues. In addition, hydrogen-rich saline treatment reduced caspase-3 activity in cortex and hippocampus after cardiac arrest/resuscitation.Hydrogen-rich saline treatment improved survival and neurological outcome after cardiac arrest/resuscitation in rats, which was partially mediated by reducing oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
ClNa | |
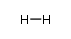 |
Hydrogen
CAS:1333-74-0 |
H2 |
|
Salicylic acid signaling controls the maturation and localiz...
2014-08-01 [Mol. Plant 7(8) , 1365-83, (2014)] |
|
Mechanism of human PTEN localization revealed by heterologou...
2014-12-11 [Oncogene 33(50) , 5688-96, (2014)] |
|
Functional consequence of the MET-T1010I polymorphism in bre...
2015-02-20 [Oncotarget 6(5) , 2604-14, (2015)] |
|
Aptamer-based polyvalent ligands for regulated cell attachme...
2015-04-13 [Biomacromolecules 16(4) , 1382-9, (2015)] |
|
Melatonin-mediated Bim up-regulation and cyclooxygenase-2 (C...
2015-04-01 [J. Pineal Res. 58(3) , 310-20, (2015)] |